
The first part of this lesson involves a study of the relationship between the shape of a v-t graph and the motion. As we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a velocity vs. but we are gathering information!)įinally, we can see that the distance is actually increasing each second.distance per second increasing, in other words can be said as: velocity is increasing. Lesson 4 focuses on the use ofvelocity versus time graphs to describe motion. Lesson 2-1 In order to better understand how sea turtles migrate through the oceans, marine biologists attach satellite-tracking devices to turtles’ shells.

(again, this rules out none of the graphs :/. Lesson 2-1 Describing Motion with Graphs (cont.) The line on this distance-time graph represents an object traveling at a constant speed. So we now know we are looking for a graph where time is increasing and there is velocity of any kind present.

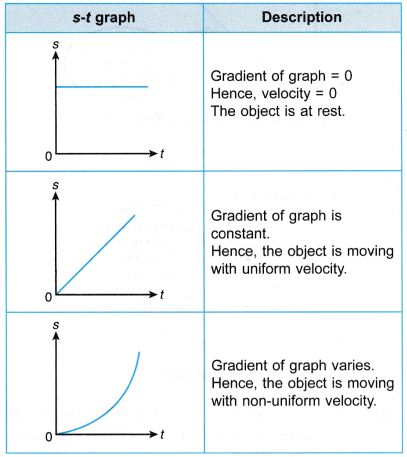
another word for distance/second is velocity. However, as you can clearly see from the diagram, with each second that passes, the fly is moving a distance. Example: For better understanding, let us consider an example of uniform motion. If we record distance and time for the motion of a body and plot the same data on a rectangular graph, we will obtain a distance-time graph corresponding to the motion of that body. From this we know we are looking for a graph with time increasing. We deal with the distance-time graph while studying the motion of bodies. As each second passes, the fly is moving. Here's a very bare bones basic way to look at this problem which may help with your understanding of time and velocities relationship in general :)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
